An electrical circuit is made up of different elements that are broadly categorized into active and passive elements. Active elements are circuit elements that can provide and amplify electrical energy. An active element is also known as an energy source. Passive elements are just opposite to active elements; they do not provide any energy; instead, they consume, store, or dissipate electrical energy.
Based on dependency on the other circuit elements, there are two types of energy sources,- Independent sources.
- Dependent sources or Controlled sources.
- Voltage-dependent voltage source.
- Current-dependent voltage source.
- Current-dependent current source.
- Voltage-dependent current source.
- Voltage-dependent voltage source.
- Current-dependent voltage source.
- Current-dependent current source.
- Voltage-dependent current source.
Independent Source:
An energy source whose output doesn't depend upon, controlled, or influence by any other element in the circuit is called an independent source. An independent source can either be a voltage source or a current source.
Voltage Source:
An independent voltage source generates a voltage across its terminals which is independent of any other voltage or current in the circuit. Some examples of voltage sources are batteries, alternators, dynamos, etc.
An ideal voltage source produces a specified voltage and current depending on the circuit conditions. The voltage remains constant irrespective of the current drawn and load connected. The voltage across the load terminals will be the same voltage generated by the source, i.e., the internal resistance of the source will be zero.
However, in a practical voltage source, the voltage doesn't remain constant and has drooping load characteristics due to some internal resistance. Whenever a load is connected across a practical voltage source, the voltage across the load doesn't remain same as the source voltage due to a voltage drop in the source itself.
A practical voltage source can be represented by an ideal voltage source in series with resistance which will be the internal resistance of the source as shown above. Generally, internal resistance is very small for a voltage source and is zero in case of an ideal voltage source.
Current Source:
An independent current source supplies a specified current independent of voltage across the source. In case of an ideal current source, the current supplied to the load remains constant and voltage depends upon the circuit conditions. Photoelectric cells, current regulators, transistors, etc., are examples of current sources.
In practice, a current source cannot deliver a constant current due to internal resistance which causes a drop in the current when connected across the load. The drop in electrical energy depends upon the internal resistance, the smaller the internal resistance, source is more closer it is to an ideal source.
A practical current source can be modeled by connecting a resistance in parallel with an ideal current source as shown above. The internal resistance is very high for a practical current source whereas it is infinite in the case of an ideal current source.
Dependent Source or Controlled Source:
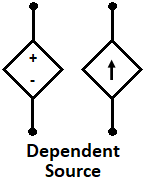
An energy source whose terminal voltage or current depends upon some other voltage or current in the circuit is called a dependent source. In other words voltage or current in a circuit is controlled by changing some other voltage or current of the circuit. The dependent source is also called a controlled source and is represented by a diamond-shaped symbol as shown in the below figures.
There are four types of dependent sources,- Voltage controlled voltage source.
- Voltage controlled current source.
- Current controlled voltage source.
- Current controlled current source.
Voltage Controlled Voltage Source:
A dependent source one whose voltage depends upon or is manipulated by another voltage is called a voltage controlled voltage source. An opamp (operational amplifier) in an inverting mode of connection is an example of a voltage controlled voltage source where the output voltage depends upon the input voltage.
Above figure shows an opamp inverting mode of connection and the circuit as voltage controlled voltage source. It can be written as output voltage Vo is equal to,
Current Controlled Voltage Source:
A dependent source one whose voltage depends upon or is manipulated by another current flowing in an element of the circuit is called current controlled voltage source. A current-feedback amplifier is an example of a current controlled voltage source, where the output voltage is proportional to the input current generally fed from a feedback network converting the input current to an output voltage.
The output voltage is determined by the input current and feedback resistor Rf placed between the output and the negative input,
Current Controlled Current Source:
In a current controlled current source, the output current of the source depends upon the current flowing in an element of the circuit. An opamp can also be used in a current controlled current source, where the output current is controlled. Below figure shows the opamp in current controlled current source.
If load resistance RL is very small, the output current Io is given by,
Voltage Controlled Current Source:
In a voltage controlled current source, the output is controlled by an input voltage. A transconductance amplifier is a voltage controlled current source, where the current produced at its output is proportional to its input voltage.
Comparison of Independent and Dependent Sources:
| Independent Source | Dependent Source | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Energy source whose output isn't affected by any other element present in the circuit is called independent source. | Energy source whose output is affected or controlled by some other element present in the circuit is called dependent energy source or controlled source. |
| Symbol | ||
| Types | Independent energy sources are types, voltage source, and current source. | Dependent energy sources are four types, voltage-controlled voltage source, current-controlled voltage source, current-controlled current source, and voltage-controlled current source. |
| Applications | Generators, batteries, power supplies, etc | Transistors, amplifiers, oscillators, etc |
Conclusion:
In this article, we have learned about different types of active elements i.e., independent and dependent energy sources, and their characteristics. However dependent sources are not used as an input power supply to a circuit like independent sources, they are used in modeling the behavior of various electronic circuits.