The process by which electrical energy is converted into heat energy i.e., the production of heat by using electricity, is known as electric heating. We know that heat (fire) plays a major role in present-day civilization. There are various conventional methods by which we can produce heat. Among all the methods of production of heat, electric heating is the most superior and efficient method of producing heat.
All heating requirements for domestic purposes such as cooking, room heating, water heating, and for industrial purposes such as welding, drying, melting, and hardening can be done easily by electric heating.
An electric heating system offers various advantages such as economical, cleanliness, pollution-free, ease of control, high efficiency, automatic protection, uniform heating, less floor area, etc. Let us see the various methods of electric heating.
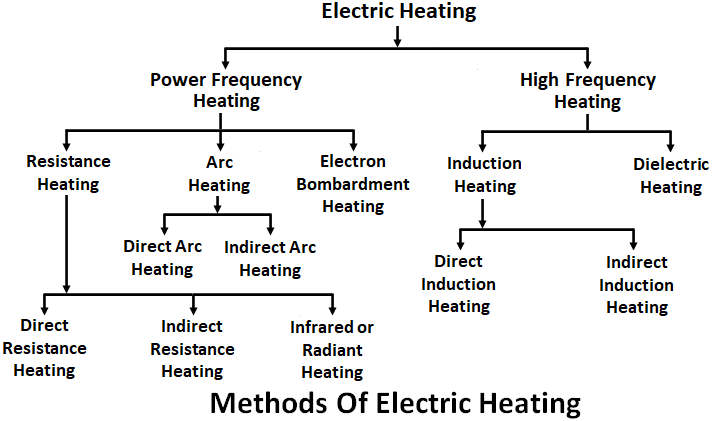
Methods of Electric Heating :
In electric heating there are various methods by which heat can be produced, the heat can be produced by passing the current through resistance or by initiating an arc between two current-carrying electrodes or by using the principle of induction or by using dielectric heating, etc. The various electric heating methods are broadly classified as follows.
Resistance Heating :
We know that there will be always a power loss in a conductor due to its resistance which results in the form of heat energy. This property of power loss due to resistance can be used for heating a substance, known as resistance heating. This type of heating has wide applications such as drying, domestic and commercial cooking, annealing and hardening of metals, etc. The resistance heating method is further classified as,
- Direct resistance heating,
- Indirect resistance heating,
- Infrared or radiant heating.
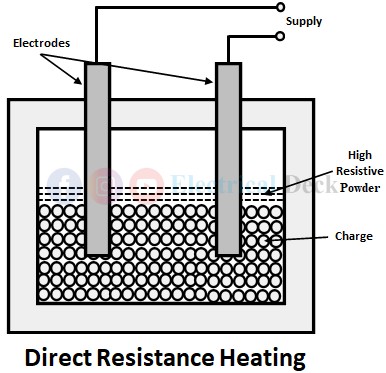
Direct Resistance Heating :
In direct resistance heating, the current is made to pass through the charge to be heated as shown below. The resistance offered by the charge to the flow of current results in the production of heat in the charge. The charge can be in the form of powder, liquid, or pieces. Since heat is produced inside the charge, this method of heating has high efficiency. This type of heating is used in electrode boiler.
Indirect Resistance Heating :
In indirect resistance heating, the current is made to pass through a high resistance element, known as the heating element. This heating element is placed above or below or around the charge to be heated. The heat produced by the heating element due to I2R loss is transferred to the charge by one or more modes of heat transfer i.e., conduction or convection, or radiation.
Infrared or Radiant heating :
In this method of heating, a tungsten filament lamp is used as the heating element together with reflectors that reflect the whole heat emitted onto the charge. The lamp used is rated between 250-1000W with a voltage rating of 120-250V and operated at 2300°c, thereby giving a large amount of infrared radiation. One of the applications of this method is drying painted surfaces.
Arc Heating :
Consider two electrodes with an air gap between them. When a high voltage is applied across two electrodes, the air between two electrodes gets ionized under electrostatic forces and thus the air gap acts as the conducting medium. Once the air gets ionized, current starts flowing through the air gap in form of a continuous spark called Arc.
Other than ionizing air to produce an arc, an arc can also be produced by short-circuiting the two electrodes momentarily and then withdrawing them back. In order to initiate an arc large voltage is required, but for maintaining an arc a small voltage is enough. By using electric arc heating, temperatures up to 3500°c can be achieved. There are two methods of electric arc heating, they are,
- Direct arc heating,
- Indirect arc heating.
Direct Arc Heating :
In direct arc heating, the arc is formed between charge and electrode or electrodes as shown below. Thus the charge to be heated will act as the second electrode. Since, in this method, the arc is in direct contact with the charge, and heat is also produced by the current flowing through the charge itself. Therefore the charge can be heated to the highest temperature. The direct arc heating method is used for the production of steel.
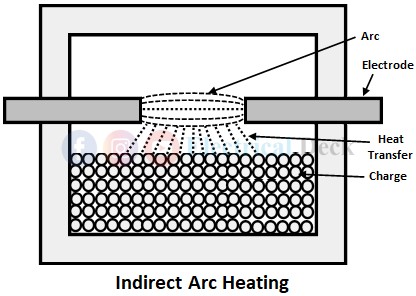
Indirect Arc Heating :
In indirect arc heating, the arc is formed between two electrodes rather than forming with the charge to be heated as shown below. The heat generated by the arc is transferred to the charge by radiation. Compare to the direct arc method, the heat produced is lower in the indirect arc method.
Since there is no flow of current through the charge, there is no inherent stirring action in the charge which can be done in the direct arc heating method. The indirect arc method of heating is suitable for melting non-ferrous metals and iron foundries.
Induction Heating :
The principle of induction heating is similar to the principle of ac transformers. It consists of two coils primary and secondary, the primary is connected to an ac supply and the secondary is used to heat the charge.
When the primary coil is energized, it induces an eddy current in the secondary due to which heat is generated. The induced eddy current depends upon, primary coil current, number of turns in primary and secondary, and coefficient of magnetic coupling.
The heat produced depends upon the power drawn by the charge. We know that power P = V2/R, thus the resistance of the charge should be low in order to develop sufficient heat, which can be possible only with metals and the voltage induced must be higher which can be obtained by employing higher flux. Thus magnetic materials are found to be suitable for induction heating because of their higher permeability. The induction heating method is again classified into two types,
- Direct induction heating,
- Indirect induction heating.
Direct Induction Heating :
In direct induction heating, the charge to be heated will act as the secondary i.e., eddy current due to magnetic flux set up by the primary coil will induce directly in the charge itself. Since heat is produced directly in the charge itself, there is no wastage of heat and high temperatures can be attained. This type of induced current heating is used for melting the charge in an induction furnace.
Indirect Induction Heating :
In indirect induction heating, the eddy currents are not directly induced in the charge. There will be a heating element that acts as the secondary in which eddy currents are induced as shown below. The heat developed in the heating element is transferred to the charge to be heated by radiation or convection. This type of heating method is employed for the heat treatment of metals.
Dielectric Heating :
The process of heating non-conducting or insulating materials is known as dielectric heating. When materials such as wood, plastic, glass, etc., are subjected to an alternating electric field. There will be interatomic friction due to which heat is produced in the material, known as dielectric loss.
In dielectric heating, the insulating material to be heated is placed between two electrodes as shown above. An ac supply of high frequency is connected across the two electrodes. Since heat produced in the material is due to dielectric loss which depends upon frequency and voltage. Thus for adequate heating effect, high voltage in the range of 5kV to 20kV at a frequency of about 10-40MHz is usually employed.