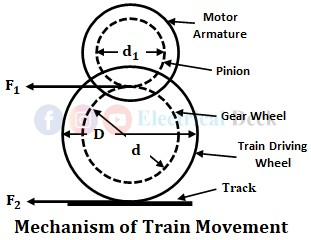
Mechanics of Train Movement :
The process of moving a vehicle by means of the driving force is known as traction. The motion of the vehicle can be obtained by transferring the tractive effort from the edge of the pinion in the motor armature to the driving wheel through the gear wheel. The driving mechanism of the vehicle is shown in the below figure.
Assume that the torque of the motor is T, then the tractive effort at pinion is given by,
T = force × distance = F1 × (d1/2)
F1 = 2T/d1
The tractive effort transferred to the driving wheel is given by,
In the above equation,- F2 = Tractive effort at driving wheel,
- F1 = Tractive effort at pinion,
- T = Torque developed by motor,
- D = Diameter of driving wheel,
- d = Diameter of the gear wheel,
- d1 = Diameter of pinion,
- η = Transmission efficiency,
- γ = Gear ratio = d/d1.
When the train is in motion, then the frictional force between the wheel and track depends upon adhesive weight and adhesive coefficient and is given by,
- μ = Coefficient of adhesion between track and driving wheel,
- W = Adhesive weight.
Coefficient of Adhesion :
The coefficient of adhesion is defined as the ratio of tractive effort to slip the wheels and adhesive weight.
The coefficient of adhesion decreases with an increase in speed. The below table shows the variations in the coefficient of adhesion with speed on dry rails.
| Speed in kmph | 0 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient of Adhesion | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.10 |
With clean dry rails, the coefficient of adhesion is 0.25. The coefficient of adhesion for wet or greasy rails is 0.08. The coefficient of adhesion of electric traction is higher than steam traction. So, an electric train can accelerate quickly.
In order to obtain rapid acceleration and high tractive effort, the coefficient of adhesion should be maintained high. Whenever the tractive effort goes higher than (μ × W) then slipping will occur. In order to avoid this kind of situation, the tractive effort should be maintained equal to or less than (μ × W).