In most industries, the prime movers (drive) used to run the machines will be an electric motor. Because an electrical motor is far superior in performance when compared to steam and diesel engines.
Depending upon how the electric motor is used in industrial applications, electric drives may be classified into three types, individual drive, group drive, and multi-motor drive. In this article, let us learn about individual and group drives with their advantages, disadvantages, and difference between them.
Individual Drive :
If in a system, only a single electric motor is used to drive or impact energy for working of a single machine then that single electric motor used comes under the category of Individual Drive. By using the individual drive, a safer operation can be performed.
Individual drives are applicable where constant speed is required such as in paper mills and the textile industry. This drive is also used in single spindle drilling machines, various types of electrical hand tools, and some metal-working machine tools.
Individual drives are the only choice for driving heavy machines such as cranes, lifts, lathes, etc. In many individual drive applications, the electric motor forms an integral part of the machine.
Advantages of Individual Drive :
- The power factor of the individual drive is high.
- High efficiency of the system is achieved.
- Machines can be located at convenient places.
- Continuity in the production of the industry is ensured to a higher degree.
- By using the individual drive, it is possible to operate a machine at the most efficient speed, start it up in minimum time, and easily reverse the direction of rotation.
- Disconnection of individual drive or its failure will not affect the working of other machines.
- The maintenance of line shafts, bearings, pulleys, belts, etc., required in group drive are eliminated here.
Disadvantages of Individual Drive :
- Individual drives cannot be employed for applications where a sequence of operations is required.
- A large system employing individual drives will require a high initial cost.
Group Drive :
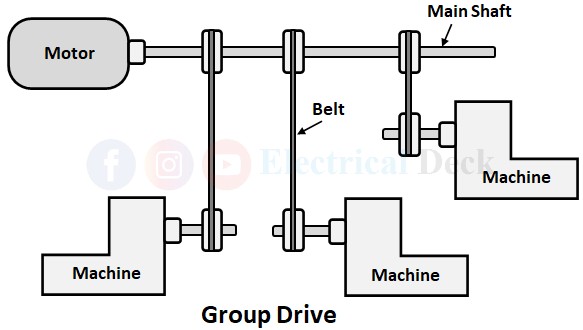
If in a system, a single electric motor is used to drive two or more than the two machines from line shafting by means of belts then this electric motor comes under the category of Group Drive. The line shaft is fitted with pulleys of different diameters which are connected to the shafts of driven machines through the belts.
The belts serve to vary their speed. Group drive sometimes is also known as line shaft drive. Group drives are employed in industries that switch over from non-electric drive (oil or steam engine) to electric drive where only the engine is replaced by a motor and retaining the rest of the power transmission system.
Advantages of Group Drive :
- A single motor of a given HP requires less cost when compared to the cost of many motors of the same aggregate HP i.e., the initial cost of a group drive is less when compared to the initial cost of the individual drive.
- Group drive has a high overload capacity.
- Group drive requires less maintenance and hence the maintenance cost is low.
- A system employing group drive requires less space as these drives occupy less area when compared to individual drives.
- In certain industrial processes, the sequence of continuity to operation is important even while starting and stopping. For such processes, group drives are the most preferred.
Disadvantages of Group Drives :
- The power factor of group drive is poor.
- Constant speed control cannot be achieved by using a group drive.
- Energy transmission and speed control through pulleys are quite cumbersome and inefficient.
- A fault on the driving motor will bring all machines connected to that motor to a standstill.
- The installation of machines should be in a manner such that they should suit the layout of the line shafting, as a result, the flexibility of layout is lost.
- Due to the energy transmitting mechanism, a considerable amount of energy is lost.
Difference Between Individual Drive and Group Drive :
| Individual Drive | Group Drive |
|---|---|
| Individual drives must be placed near the machines. | Group drives can be placed outside the workshop. |
| These drives don't affect the working of other machines. | These drives affect the working of other machines i.e., failure in one drive will result in failure of the complete machines connected to it. |
| These drives are more efficient. | These drives are less efficient. |
| Individual drives are easy to repair. | Group drives are difficult to repair. |
| Requires more maintenance. | Require less maintenance. |
| Individual drives are more flexible. | Group drives are less flexible. |
| Due to the presents of each drive for each machine, these drives require more space. | Group drives require less space due to the presents of one drive for two or more machines. |
| Chances of accidents are less in the individual drive. | Chances of accidents are more in group drives. |
| Less power consumption if fewer machines are in operation. | More power consumption if fewer machines are in operation. But economical when all machines are in operation. |
| Line shaft is not required. | Requires line shaft. |
| The initial capital investment required for the individual drive is high. | Less initial capital investment. |
| Speed control of each machine can be done easily. | Speed control of each machine in a group drive is not easy. |
| The direction of rotation of the shaft of each machine can be changed easily as per requirement. | It is difficult to change the direction of rotation of the shaft of each machine in the group drive. |