Both electrical science and the practical applications of electricity began with direct currents and its first practical application was DC Telegraphy powered by electrochemical batteries. Electrical lighting also began with dc power using dynamos. The first electrical central station was built by Thomas Alva Edison at pearl street in new york and it began in the year 1882 with operating dc voltage at 110 volts.
Nowadays, modern civilization mainly depends on the consumption of electrical energy for domestic, industrial, commercial, and agricultural applications. For this purpose, an efficient transmission system is very necessary since the generating stations are located in remote areas. An efficient transmission system has to meet the following requirements.
- Bulk power transmission over long distances,
- Low transmission losses.
- Less voltage fluctuations.
- Possibility of power transfer through submarine cables.
- System of interconnection.
Up to the 1980s, ultra high voltage ac (UHV-AC) transmission lines above 765 kV were used for bulk power transmission, and due to the development of accurate control in thyristor, the HVDC (high voltage direct current) transmission lines are using which are having a distinct superiority over UHV-AC transmission lines.
What is HVDC Transmission System?
The High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission system uses direct current for the transmission of power over long distances. The HVDC transmission system provides efficient and economic transmission of power even to very long distances that meet the requirements of growing load demands. Due to its simple constructional feature and less complexity, research and development authority discovered its usage in modern power transmission.
By comparing ac and dc transmission, it is clear that for transmission of power over long distances ac is not much suitable, and for generation and utilization of power, dc is not favorable compared to ac.
Thus, for HVDC transmission it requires terminal equipment for convening ac into dc at the sending end, and terminal equipment is again required at the receiving end to invert this dc supply obtained into ac.
Principle of HVDC Transmission System :
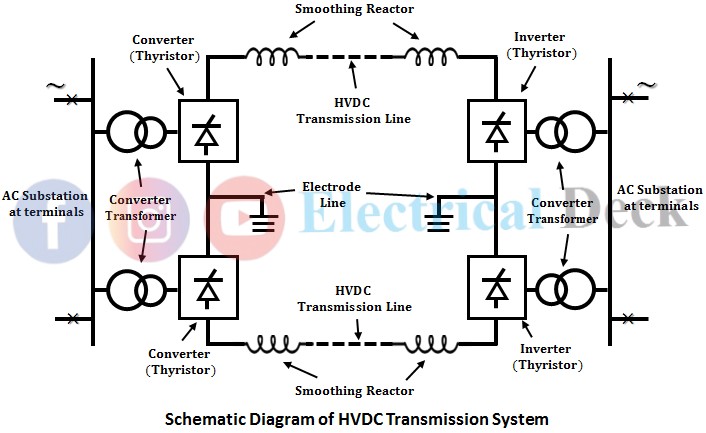
The HVDC transmission system mainly consists of converter stations where conversions from ac to dc (rectifier station) are performed at sending end and at the receiving end the dc power is inverted into ac power using an inverter station. Hence, the converter stations are the major component of the HVDC transmission system.
Also, by changing the role of the rectifier to inverter and inverter to rectifier the power transfer can be reversed which can be achieved by suitable converter control. The below shows the schematic diagram of the HVDC transmission system.
The ac substations at both ends of the HVDC line consist of ac switchgear, bus bars, current transformers, voltage transformers, etc. The converter transformers are connected between converter values and ac bus valves which transfers power from ac to dc or vice-versa.
Smoothing reactors are necessary for converter operation, and for smoothing the dc current by reducing ripples obtained on the dc line. The electrode line connects the midpoint of converters with a distant earth electrode.