The overhead lines and underground cables are methods used for the transmission and distribution of power in an electrical power system. The selection of overhead line or underground cable depends upon various factors like operating voltage, amount of distance the power to be transmitted, initial cost, maintenance cost, condition of land through which the line is to be passed, etc.
By considering these factors either overhead lines or underground cables are selected for transmitting the power. Let us see the differences between overhead and underground systems used for the transmission and distribution of electrical power.
Comparison Between Overhead Lines and Underground Cables :
| Characteristic | Overhead lines | Underground Cables |
|---|---|---|
| Initial cost | Less | For the same power transfer, the cost is double as compared to overhead lines |
| Public safety | Less | More |
| Maintenance cost | More | Less |
| Occurrences of faults | More | Less |
| Frequency of accidents | More | Very less |
| Appearance | Not good | Good looking |
| Identification of faults | Easy | Very difficult |
| Interference to communication lines | Affected | No effect |
| Voltage drop | More | Low |
| Damage due to lightning and thunderstorms | Affected | Free from lightning and thunderstorms |
| Jointing of wire/cables | Easy | Very difficult |
| Operating voltage | Used for any range i.e., 756kV or even higher | Up to 132kV |
| Charging current | Less | More (since the spacing between conductors is less) |
| Surge effect | More | Less |
Overhead Lines :
The overhead transmission and distribution line system is the most widely used method of transmitting and distributing electrical power from one place to another place.
It is the only method used for transmitting a large quantity of electrical power over longer distances i.e., power transmission between power station and substation, or between substations. The various components of overhead lines include supports, cross-arms, insulators, conductors, stays, guys, lightning arrestors, fuses, isolating switches, earth wire, guard wires, etc.
Since there is no insulation coating is used over conductors, the overhead system for transmission and distribution is very cheap compared to the underground system.
But the use of overhead lines includes drawbacks like they are liable to hazards from lightning discharges, public safety is less, problems due to interference with neighboring communication lines, difficulty to use near submarine crossings, etc.
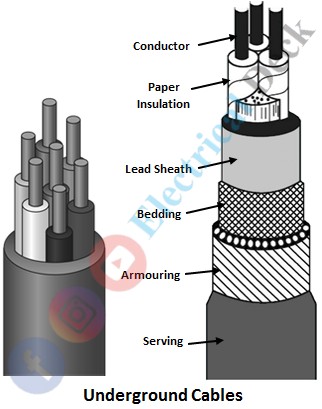
Underground Cables :
Electrical power can be transmitted and distributed either by the overhead system or by underground cables. The underground cables have several advantages such as rugged construction, greater service reliability, increased safety, lesser chances of faults, low maintenance cost, better appearance, and lesser interference from external disturbance like storms, lightning, ice, trees, etc, as compared to overhead system.
However, the use of underground cables have a greater installation cost, also insulation problem arises at high voltages with cables. Hence, power transfer throw cables are used where it is impracticable to use overhead lines.
Earlier days underground cables were mainly used in thickly populated areas and that to these are limited for low and medium voltages only, but nowadays due to requirements even Extra High Voltages for longer distances.
The use of underground cables for power transmission reduces (mostly eliminates) the possibility of supply interruption due to lightning. For long-distance power transmission, cables can not be used due to their large charging currents.