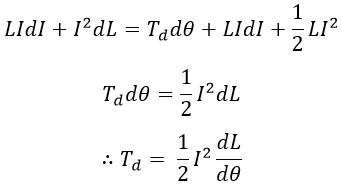The moving iron type instruments are one of the types of measuring instruments used for measuring voltage or current. These instruments use a movable piece of iron placed in the magnetic field that deflects the pointer over the scale and hence named moving iron instrument.
There are two types of moving iron (MI) instruments. They are, attraction type and repulsion type moving iron instruments. In this article let us learn about attraction type moving iron instrument.
The working principle of attraction type moving iron instrument is based on magnetic attraction, which attracts an iron piece when placed near a magnet field. Here, the magnet field will be produced by an electromagnet.
Construction of Attraction Type Moving Iron Instrument :
It consists of a fixed coil that is flat with a narrow opening in it. A moving iron that is made of soft iron is mounted on a spindle. The coils are wound with a number of turns that depend upon the range of the instrument. The pointer is mounted on a spindle which consists of a graduated scale for showing the deflection. The construction of attraction type moving iron is shown below.
The controlling torque is provided by the springs or if the instrument is vertically operated gravity control can also be employed. This instrument uses air friction damping to damp out oscillations which consist of a movable piston made of aluminum placed in an air chamber.
Since the operating magnetic field produced by the coil winding is not much strong, the eddy current damping which uses permanent magnets can distort the main field. Thus eddy current damping cannot be used and fluid friction damping is not much preferred. The moving iron is made of sheet metal for obtaining a uniform scale.
Working of Attraction Type Moving Iron Instrument :
Whenever coil winding is connected across the supply to be measured, it setups a magnetic field. The intensity of the magnetic field is higher inside the coil compared to the intensity of the outside, and hence low reluctance exists inside the coil.
As the moving iron tries to occupy the low reluctance position, it is moved and gets attracted to the fixed coil. As the iron piece moves, the pointer also moves to show the deflection. The instrument attains the equilibrium position when controlling torque balances the deflecting torque.