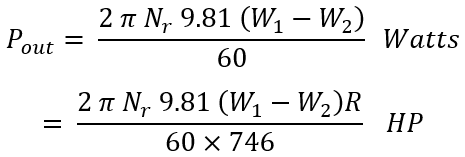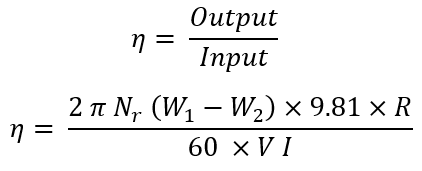In the last article, we have seen Swinburne's Test of dc machine, where the efficiency and losses are determined without applying actual load on the machine. It is an indirect method of testing a dc machine. Now let us see another method of testing a dc machine called 'Brake Test'.
Brake Test of DC Machine :
In the brake test, the dc machine is tested by actual loading with the help of breaks. Since the load is applied directly to the machine shaft, it is a direct method of testing a dc machine. The determination losses and efficiency of a dc machine are done by performing a brake on the shaft through belt and pulley arrangement.
The arrangement for performing a brake test on a dc motor is shown below. A water-cooled pulley is attached to the shaft of the motor. In the case of a brake test on a dc generator, an electrical load is applied at the generator terminals.
The brakes on the rotating pulley are applied through a belt placed on the pulley. One end of the belt is attached to a known weight of wooden blocks with help of rope gripping the pulley. The other end of the belt is fixed to the floor through a spring balance. Let us consider, the weight suspended through wooden blocks be W1 (i.e., known weight) and readings from the spring balance be W2.
When the motor is connected across the supply. By varying the weight of the wooden blocks on the motor, the load is adjusted till it carries full-load current. The load on the motor shaft is varied step by step up to its full-load current. In the process, at each step of increasing load, the readings of the voltmeter, ammeter, speed of the motor, and the suspension weight (W1 and W2) are noted.
If the reading from spring balance is W2 kgf and the suspended weight from wooden blocks is W1 kgf. The net pull by the belt applied on the pulley due to friction is,
If Nr is the speed of the motor or pulley in rpm and R is its radius in meters. Motor power output is given by,