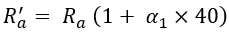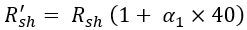For small ratings of dc machines, we can perform the tests directly by loading. In the case of large dc machines, it is difficult to perform tests by loading directly. For this purpose, there are indirect methods of testing a dc machine without actually loading the machine so that losses and efficiency can be calculated at any desired load. The most commonly used indirect methods of testing dc machines are,
- Swinburne's Test
- Hopkinson's Test
In this article let us discuss briefly Swinburne's test and how it is performed.
Swinburne's Test of DC Machine :
It is an indirect method (without actual loading) of testing the dc machine where the losses are calculated and efficiency can be determined at any load either the machine running as a generator or motor.
Since the test is performed without loading the machine it is also known as No-load Test. However, without load, we cannot start a dc series motor. Hence this test is limited for dc shunt and compound machines where flux remains practically constant.
The connection diagram for Swinburne's test is shown above. At no-load with rated voltage, the machine runs as a dc motor. By adjusting the rheostat connected in series with the shunt field the motor speed is adjusted to its rated value.
Let,- V = Input supply voltage
- Ia = No-load armature current
- Ra = Armature resistance
- Ish = Shunt field current
- Rsh = Shunt field resistance
- Power input = V I (Ia + Ish) watts
Since it is a no-load test there is no output at the motor, but the input as to supply,- Iron loss or constant loss,
- Friction and windage loss,
- Copper loss in the shunt field (Ish2 Rsh), and
- Armature copper loss (Ia2 Ra).
Since, the iron, friction, and windage losses are independent of load. The losses remain constant throughout the operation i.e., at any load. Constant losses Wc are obtained by subtracting the shunt field copper loss and no-load armature copper loss from the no-load input.
Here, the copper loss will not remain constant through the operation. As the load on the motor varies the temperature of the field and armature winding increases, this affects their winding resistances. If Ra' and Rsh' are the new resistances due to a change in temperature. Consider, that the temperature change is about 40⁰.