Principle of Operation of AC Series Motor :
An ordinary dc series motor will run in the same direction regardless of the polarity of the supply. The direction of the torque depends upon the relative directions in space of flux and armature current. If the line terminals are reversed, both the field and armature current are reversed, and the direction of torque remains unchanged. Therefore, the motor continues to rotate in the same direction.
So when normal dc series motor is connected to an ac supply, both field and armature currents reverse simultaneously and unidirectional torque is produced in the motor.
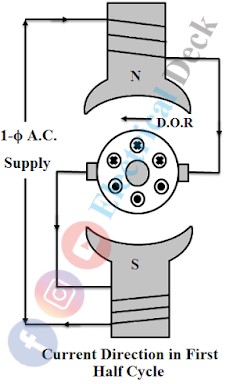
Consider the case of a two-pole motor and let the alternating current be in its positive half, then the polarity of the field poles and the currents flowing through the armature conductors be as indicated in Figure.
The armature conductors carry inward currents +ve under N-pole and outward currents -ve under S-pole. By applying Fleming's left-hand rule it will be seen that the torque developed in the armature will try to rotate in an anti-clockwise direction.
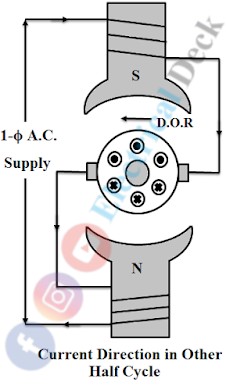
During the next instant, the alternating current goes through the negative half cycle Now the current through the field winding and armature will also change. It will be again seen that the armature will tend to rotate in the same direction because of the uniform torque produced by the two halves of the cycle.
Thus a series motor can run on both the dc supply and ac supply. The performance of dc Series motor works on ac supply is not satisfactory due to the following reasons,
- The efficiency is low. This is because of the increase in core losses due to alternating flux.
- The reactance of the field and armature winding increases as the supply given is alternating, which makes the machine run at a low power factor.
- Considerable sparking at brushes will occur. This is due to poor commutation. The voltage induced by transformer action in the coil undergoing commutation further intensifies commutation difficulties.
Constructional Features :
Modification in Design of AC Series Motor :
Some modifications are required to have a satisfactory performance of dc series motor on a.c supply, when it is called as ac series motor. The modifications are :- Fully laminated poles and yokes must be used in order to reduce eddy current losses.
- The power factor can be improved by reducing field and armature reactances. In order to reduce field reactance, the field winding is designed with less number of turns. Lower pole flux also reduces the transformer emf in the commutating coil.
- The motor should be provided with a large number of poles each supplying less flux per pole.
- A reduction in the number of turns on the field winding would also reduce field flux. To keep the torque constant on the shaft, the armature turns should be increased proportionately. This increases the armature reaction and armature reactance.
- Compensating winding should be employed to lower the armature reactance as far as possible. Compensation also improves commutation. The flux produced by compensating winding is opposite to that produced by the armature and effectively neutralizes the armature reaction.
- The armature coils are single turn coils and brushes of less width are used not to short circuit more than two coils at a time.
- The air gap is made very small so that fewer field turns can be used per pole.
- The frequency of supply used is reduced. The transformer emf is proportional to frequency and hence good commutation is easy at lower frequencies.
Characteristics of AC Series Motor :
The characteristics of ac series motor is similar to that of dc series motor. The torque is proportional to the square of the armature current and speed is inversely proportional to the armature current.
The series motors must always be started with some load on them because the starting speed of the motor is very high due to high starting torque i.e., 3 to 4 times the full load torque.